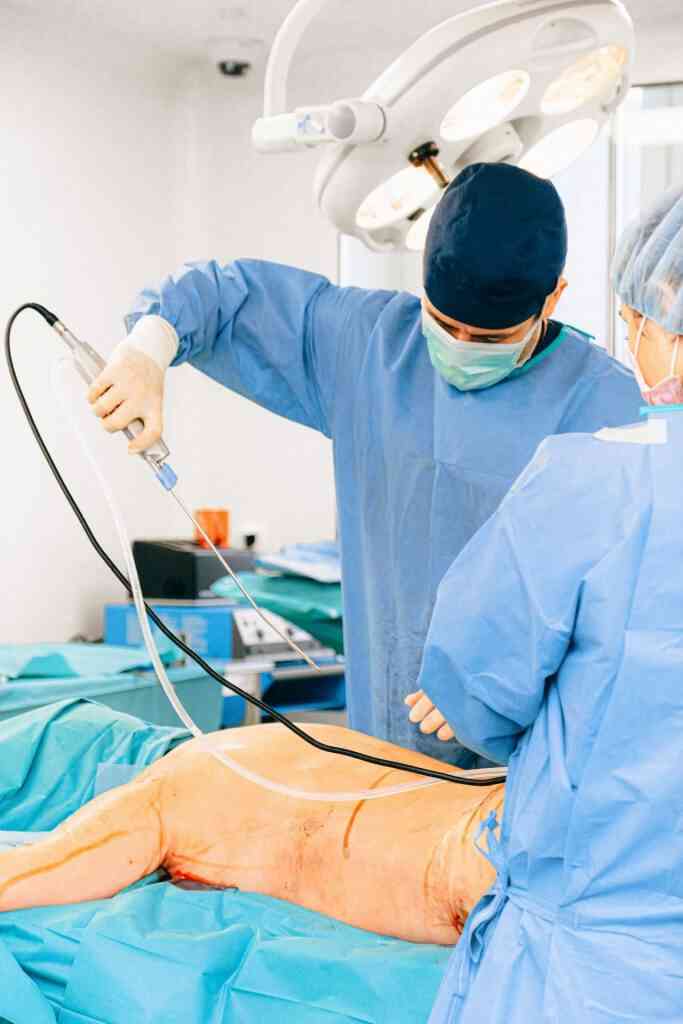
Robotic Surgery Revolutionizes Cancer Treatment in Kerala: A Comprehensive Overview
In a groundbreaking initiative, the Regional Cancer Centre in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, has secured $7 million in funding to establish a state-of-the-art robotic surgery facility, marking a significant milestone in cancer care in India. This remarkable achievement brings the transformative benefits of robotic surgery to a public hospital setting, expanding access to this advanced treatment modality for patients in the region.
The Significance of Robotic Surgery in Cancer Treatment
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery (RAS), has emerged as a game-changer in cancer treatment, offering numerous advantages over traditional surgical methods. Its enhanced precision, superior dexterity, and improved visualization capabilities translate into tangible benefits for patients:
- Minimally Invasive: Robotic surgery involves smaller incisions, resulting in reduced scarring, less pain, and a quicker recovery.
- Reduced Hospital Stays: Patients undergoing robotic surgery typically experience shorter hospital stays, allowing for a faster return to their daily activities.
- Quicker Recovery: The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery facilitates faster healing and rehabilitation, minimizing discomfort and inconvenience.
Current Landscape of Robotic Surgery in India
Until recently, access to robotic surgery in India was limited to a select few major hospitals and healthcare institutions. In Kerala, only three private healthcare providers offered robotic surgery services: Apollo Adlux Hospital, Amrita Hospital, and Aster Medcity. All three facilities utilized the da Vinci Surgical System developed by the American company Intuitive Surgical, a global leader in robotic surgery technology.
Expansion of Robotic Surgery Services in India
The growing demand for robotic surgery has spurred its increasing adoption in major private hospitals and healthcare facilities across India. The Apollo Institute of Robotic Surgery at Apollo Hospitals and Max Healthcare’s Max Institute of Robotic Surgery are among the country’s largest robotic surgery programs. These facilities employ various robotic surgery systems, including da Vinci, Renaissance Robotic Technology, and CORI Surgical System by Smith+Nephew.
Other private institutions have also embraced robotic surgery to provide advanced care to their patients. Venkateshwar Hospital in Delhi utilizes the Hugo RAS System, while Swagat Hospitals in Northeast India operates a robotic surgery theatre equipped with CMR Surgical’s Versius System.
Robotic Surgery Market in India: A Promising Future
The robotic surgery market in India has witnessed steady growth over the years, with its value projected to reach approximately $300 million in 2024. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for minimally invasive surgical procedures and the technological advancements in robotic surgery systems.
Factors Contributing to the Growth of Robotic Surgery in India:
- Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases: The increasing incidence of chronic diseases, including cancer, has fueled the demand for advanced surgical techniques like robotic surgery.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in robotic surgery systems have enhanced their precision, dexterity, and visualization capabilities, making them more attractive to surgeons and patients alike.
- Government Initiatives: Government initiatives aimed at improving healthcare infrastructure and promoting access to advanced medical technologies have contributed to the growth of robotic surgery in India.
Affordable Alternatives in Robotic Surgery
Recognizing the need for more affordable robotic surgery options, Indian cardiologist Dr. Sudhir Srivastava developed the SSI Mantra, a locally made robotic surgery system. Priced significantly lower than its competitors, the SSI Mantra was commercially launched in 2021 and aims to make and sell over 1,000 units by the end of the decade. Currently, it is installed and operational in five hospitals across India: Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute in New Delhi, Continental Hospital in Hyderabad, Sanjeevani CBCC USA Cancer Hospital in Raipur, Hindustan Hospital in Coimbatore, and Cytocure Hospital in Mumbai.
Conclusion
The establishment of a robotic surgery facility at the Regional Cancer Centre in Thiruvananthapuram marks a significant milestone in cancer care in India. This initiative, made possible through the Rebuild Kerala Initiative, brings the benefits of robotic surgery to a public hospital setting, expanding access to this advanced treatment modality for patients in the region.
As robotic surgery continues to gain popularity, it is imperative to ensure equitable access to this technology across all socioeconomic strata. By promoting affordable alternatives and encouraging the adoption of robotic surgery in more healthcare institutions, India can harness the full potential of this innovative technology to improve cancer care outcomes and enhance the quality of life for patients battling this challenging disease.